Bangladesh
In order to achieve Universal Health Coverage, access to quality healthcare for everyone is fundamental. In Bangladesh, private sector health services are expensive and out of pocket expenditures for healthcare are high. Quality of care in both public and private services is poor, with assessments of the quality of provider care reporting low levels of professional knowledge and poor application of skills in practice.
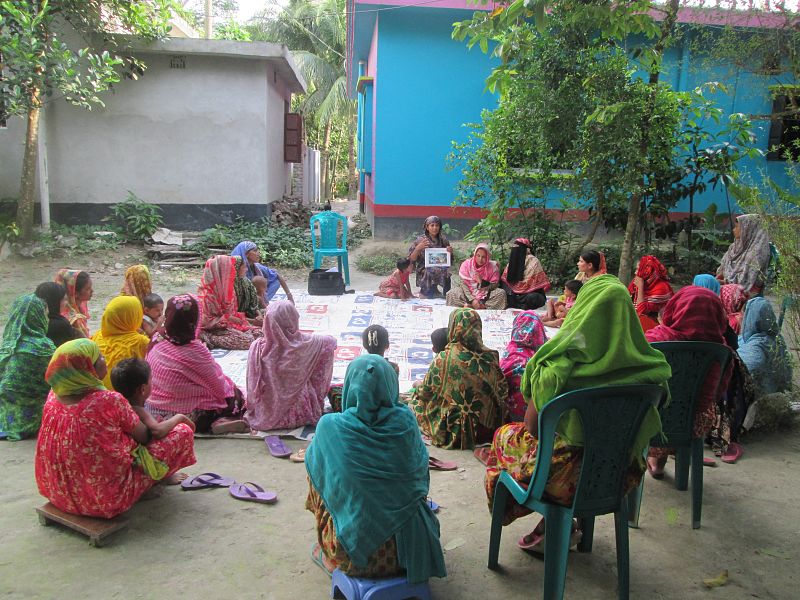
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a growing global concern. In Bangladesh, it is a major concern, as the country is a major contributor to the issue, compounded by the overuse of antimicrobials and limited understanding of the dangers of AMR. In March 2018, with Global Challenges Research Fund (GCRF) support, the University of Leeds, ARK Foundation, Malaria Consortium and the University of Liverpool conducted a household survey on the use of antibiotics among 1,301 adults in 26 villages of Comilla district, Bangladesh. The results suggest that awareness of antibiotics is limited among the general population, but that antibiotic use is common.
Malaria Consortium in Bangladesh
Antimicrobial resistance is a growing threat to global health that threatens to reverse decades of progress across the health and environmental sectors. In partnership with Nuffield Centre for International Health and Development, University of Leeds and ARK Foundation, we undertook a study in Comilla District, Bangladesh, exploring the feasibility and acceptability of using a Community Dialogue Approach to improving appropriate use of antibiotics at community level.
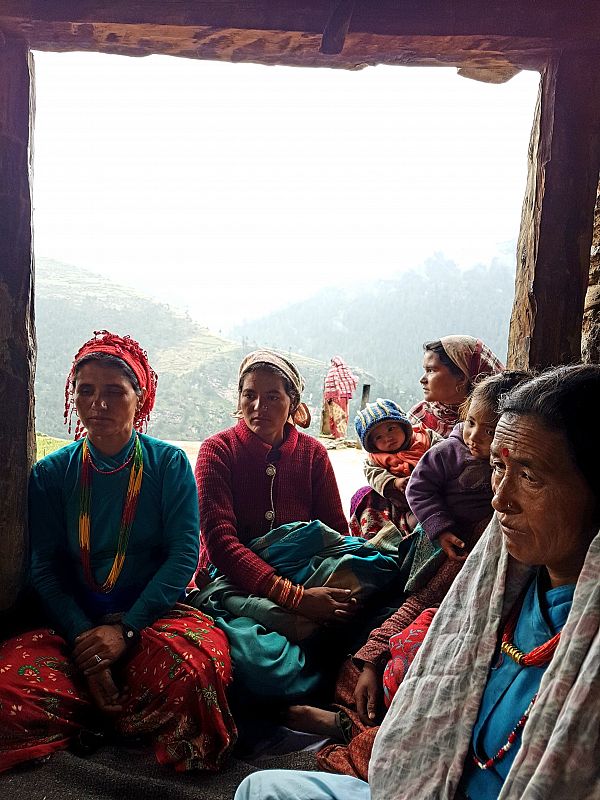
To date, effective and sustainable engagement (CE) interventions that address the contextual drivers of AMR through a One Health approach have not been evaluated and scaled up. To build on our pilot study, we are currently undertaking a project to implement and evaluate an innovative Community Engagement intervention in Bangladesh and Nepal.